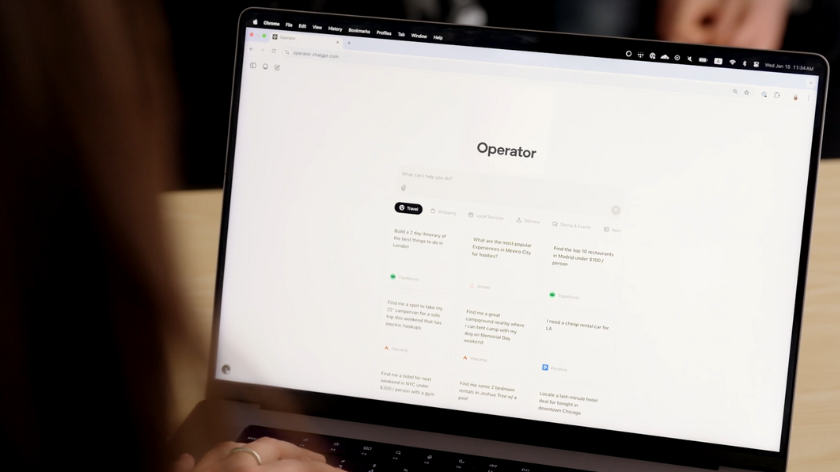
The makers of ChatGPT and o1 showcased its first agentic AI system, claiming Operator is “capable of doing work for you independently — you give it a task and it will execute it”.
Powered by a new underlying model, named CUA, Operator can interact with the buttons and menus on a screen just as a mouse would when performing a task.
Should the AI agent encounter a stumbling block, OpenAI claims Operator can correct itself, adding: “When it gets stuck and needs assistance, it simply hands control back to the user, ensuring a smooth and collaborative experience.”
Subscribe today for free
Operator can essentially perform tasks without the need to install custom APIs. Users simply describe the task they’d like it to perform and the AI agent gets to work.
OpenAI said users can take control of Operator’s browser “at any point” and that the AI agent is trained to ask the user to take over for tasks that require logging in, inputting payment details, or to solve CAPTCHAs (‘prove you’re not a robot’ tests).
Operator is, for now, limited to US-based ChatGPT Pro users, the $200 monthly plan that Sam Altman recently suggested OpenAI was losing money on.
OpenAI said the limited release window will allow it to learn from users to refine it ahead of a wider release.
OpenAI eventually plans to expand Operator to Plus, Team, and Enterprise subscriptions, as well as integrate its capabilities into ChatGPT “in the future”.
Inside Operator: OpenAI’s first steps into agentic AI
Operator marks OpenAI’s first agentic AI offering, or an agent-based AI system capable of performing assigned tasks on behalf of a user or another system — read Capacity's full explainer on agentic AI.
Agentic AI systems like Operator differ from how ChatGPT works by performing tasks you give it independently. While ChatGPT relies on information its underlying models are trained on (or through an external browser via an API call), Operator searches for the answer to a user query by itself.
Operator also works slightly differently from most other agentic AI solutions in that it works autonomously with a web browser. Traditional agentic systems, rather, work by leveraging external APIs.
OpenAI has long teased it’s AI agent work, with its ChatGPT revision last summer the first public confirmation that it was developing tools capable of independently performing tasks for users.
Before its 2024 ChatGPT rework, reports suggested OpenAI was working on agent-based solutions capable of executing multi-step tasks for users autonomously within a dedicated environment, like transferring data to a specific spreadsheet or application.
Upon unveiling Operator, OpenAI said the ability to use the same interfaces and tools that humans interact with daily “broadens the utility of AI, helping people save time on everyday tasks while opening up new engagement opportunities for businesses”.
It’s important to remember that agent-based systems like Operator should not be construed with so-called ‘artificial general intelligence’ or AGI, where an AI can think for itself — a concept straight out of science fiction which researchers are, at the earliest, decades away from developing.
Underneath Operator
Powering OpenAI’s newest agent is a new model named CUA, which stands for Computer-Using Agent.
CUA combines the visual capabilities of GPT-4o with the advanced reasoning through reinforcement learning of o1 to enable Operator to interact with on-screen environments and graphical user interfaces (GUIs), like text boxes and menus.
Operator uses screenshots of a user’s screen to identify what it’s doing to perform actions that a mouse and keyboard might perform when using the web.
OpenAI stressed the underlying CUA is still early in its development, naturally suffering some limitations. For example, the AI agent struggles with more complex interfaces like creating slideshows or managing calendars. Feedback from initial users will help enhance its accuracy, the team behind it said.
Safety and privacy: What can Operator not do?
Upon unveiling Operator, OpenAI stressed safety as its “top priority”, with the AI agent housing several layers of safeguards.
Operator is trained to ensure that the person using it is always in control, with the agent asking for inputs at certain points when performing a task.
Users can take over at any point, specifically when inputting sensitive information. OpenAI said that when a user is in takeover mode, Operator won’t collect or screenshot information entered by the user.
Before finalising any significant action, such as submitting an order or sending an email, Operator will ask for user approval.
OpenAI confirmed Operator is also trained to refuse sensitive tasks, such as banking transactions or those requiring high-stakes decisions, like deciding on a job application.
The AI agent also features a training opt-out solution — simply turn off ‘Improve the model for everyone’ in ChatGPT’s settings to prevent data sourced by Operator to not be used to improve future OpenAI models.
OpenAI also claims to have built defences against “adversarial websites” that might try to mislead Operator through hidden prompts, malicious code, or phishing attempts, with the AI agent also containing a dedicated “monitor model” that watches for potentially suspicious behaviours.
“We know bad actors may try to misuse this technology,” OpenAI said in a blog post. “That’s why we’ve designed Operator to refuse harmful requests and block disallowed content. Our moderation systems can issue warnings or even revoke access for repeated violations, and we’ve integrated additional review processes to detect and address misuse.”
Operator was unveiled mere days after OpenAI joined forces with the likes of SoftBank, Microsoft, Oracle, and MGX to launch the $500 billion AI infrastructure project, Stargate — an effort attacked by Elon Musk over claims the AI startup doesn’t have the money to support it.
RELATED STORIES
Softbank, OpenAI, Oracle & Microsoft back $500bn Stargate AI project
OpenAI officially releases text-to-video model Sora
OpenAI, Tesla mulled buying Cerebras: 4 revelations from latest Musk v OpenAI filing